What is quantum consciousness?
Quantum consciousness is a theory that proposes that quantum effects in the brain give rise to conscious awareness and free will.
These effects may help explain how we integrate the trillions of microscopic processes in our bodies into unified first-person perspectives. This allows us to observe ourselves and the world, and make decisions in a fluid feedback loop with our surroundings - choices about exploration, purpose and survival.
Nirvanic believes our conscious experience aligns well with key properties of quantum mechanics: entanglement, superposition and measurement. Our approach is to use these properties, with quantum computers, to create conscious, agentic AI systems that are aligned with human values.
Curious about our scientific program to empirically test our theory of quantum conscious agency in AI? See our FAQs.
Quantum entanglement creates a unified experience
Don’t look down. Something spectacular integrates the millions of sensory signals our nervous system processes into one coherent experience of “you” doing things, like climbing this big rock.
Entanglement is an intriguing quantum property where information in particles becomes correlated regardless of distance—across the vastness of the macroscopic brain or even the galaxy.
But this bizarre experimentally proven quantum phenomenon may help address the “binding problem” of consciousness: how a huge multitude of disparate signals from all over the mind and body are woven into a single, holistic experience.
Superposition creates a feeling of choice
If you thought quantum entanglement was odd, strap yourself in. When a quantum system is in a superposition, it has the uncanny ability to be in multiple states at the same time. While we do not fully understand why it happens at a fundamental level, we can predict and use superposition effectively in computation.
So instead of information being represented, say as neurons firing or not firing (or zeros and ones in a traditional digital computer), quantum information can represent binary states simultaneously. Superposition is what gives quantum computers the much-celebrated phenomenal speed advantage over conventional computers for specific problems.
Superposition may also be how our brain hyper-computes across a vast multitude of life experiences, relational contexts, symbols and present sensory inputs, to consider new options and consequences, all within a split second. And all on 20 watts of power. No supercomputer in the world can do that. Your brains may be quantum. So why can’t our AI?
Quantum measurement creates free will
Quantum measurement adds to the consciousness puzzle, and may be at the heart of our feeling of choosing a course of action.
Quantum measurement is the counterintuitive process by which a quantum system, previously in a superposition of states, collapses into one definite state when observed or interacted with. It was made famous by the double slit experiment that showed how particles, like electrons, exhibit wave-like interference when not observed, but behave as particles with definite paths when they are.
Our feeling of free will may be our mind making a “measurement” of our quantum system, resulting in a definite action outcome.
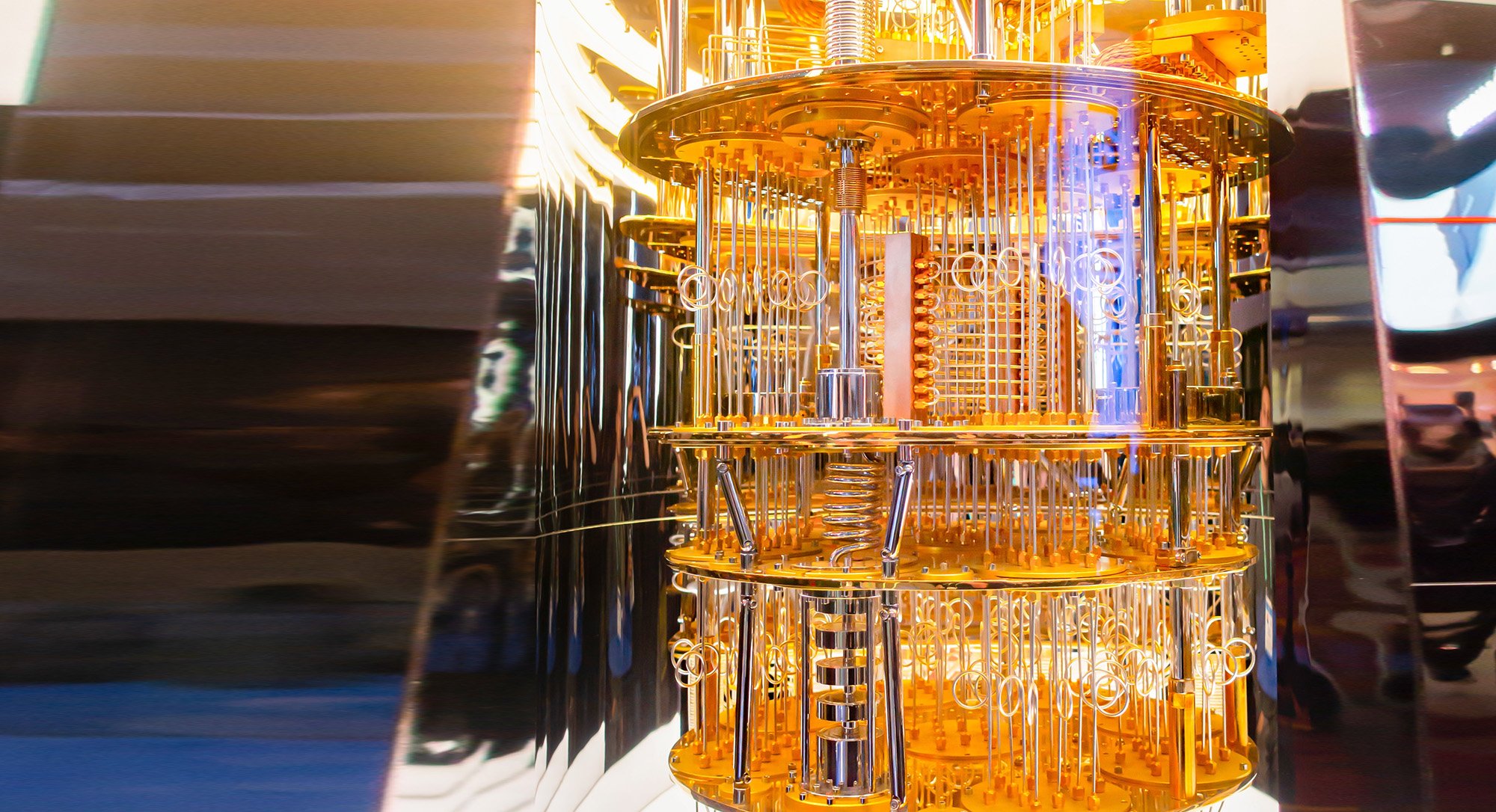
Building a Quantum Mind
Today’s quantum computers, like the IBM machine shown here, are capable of leveraging entanglement, superposition and measurement. We now have the tools to begin exploring consciousness itself. This could open up groundbreaking opportunities to replicate conscious processes in AI.
Traditional neuroscience models suggest that all thoughts, awareness, and actions stem from neurons firing in patterns similar to binary code—abstractly represented as zeros and ones. In contrast, quantum consciousness proposes that the brain performs additional forms of biocomputation, harnessing quantum properties like superposition, entanglement, and measurement. These properties allow the brain to create and process complex, exotic states of information in ways classical models cannot explain.
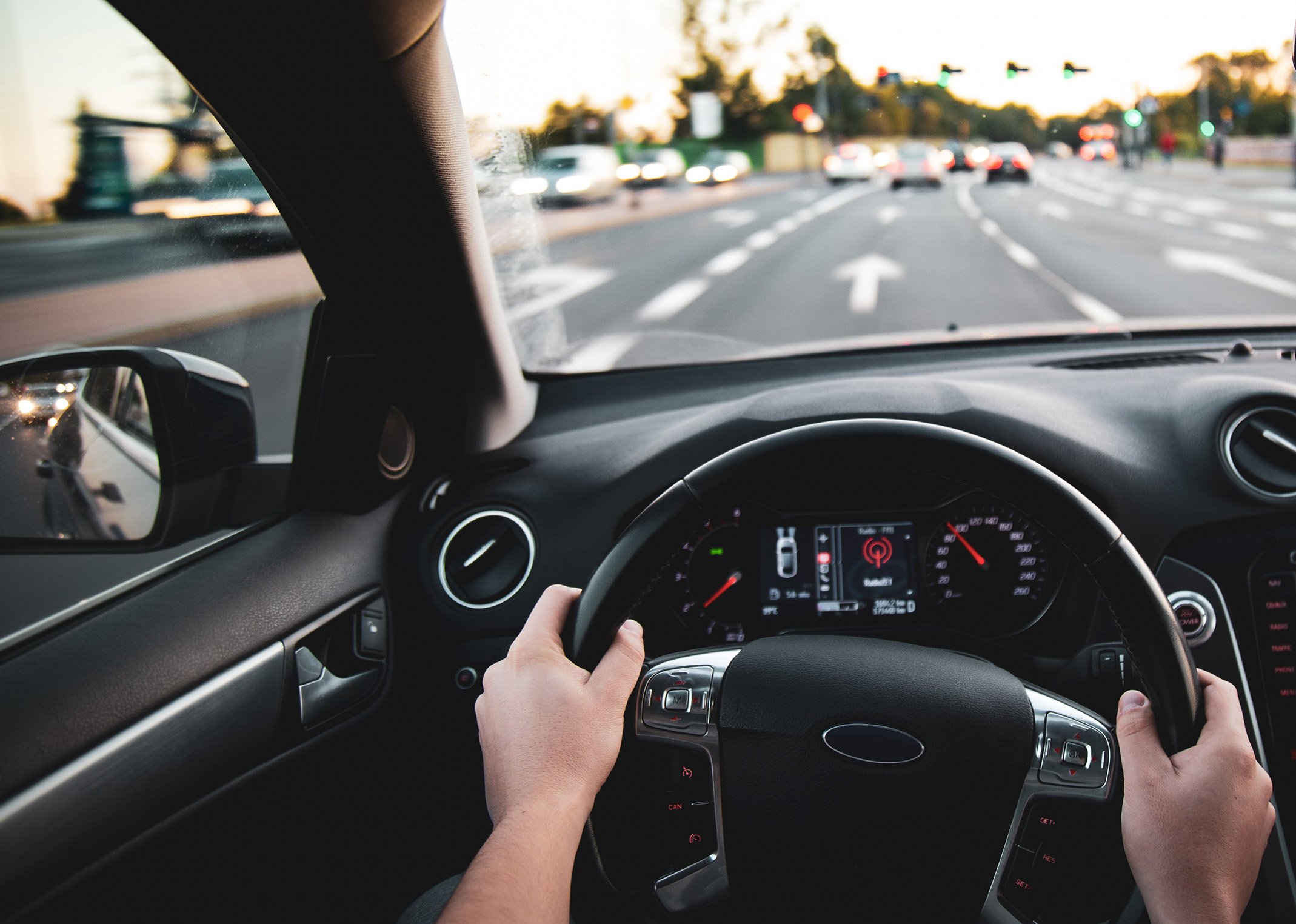

Conscious versus unconscious processes
Another important dimension in our consciousness is unconscious activity. Take driving, for example. Over time, routine actions like steering or braking become automatic, allowing experienced drivers to “zone out” and operate mostly on autopilot. These unconscious behaviors rely on classical physics and muscle memory.
But when something unexpected happens—like a truck swerving into your lane—your brain snaps into a hyper-alert, conscious state. This advanced processing enables you to quickly analyze complex data and make rapid decisions. Nirvanic believes this conscious processing leverages quantum states, helping us navigate novel, nuanced, and emotionally significant situations related to survival, exploration, and purpose.
This duality explains why we can make both automatic, unconscious decisions and deliberate, conscious ones. Competing theories fail to account for the qualitative differences between these states, making quantum consciousness a compelling candidate for a more complete theory of mind.

Consciousness helps us learn
Conscious processes are with us from the start. When we are born, we are highly conscious and self-aware even before long-term memories form. Our childlike sense of awe and wonder stems from this heightened consciousness, as we remain fully present in the moment. While some unconscious instincts, like breathing and heart rhythms, are already in built in, we have yet to learn about the world or form a sense of self.
As a child matures, we develop unconscious decision-making, similar to what AI programmers call “subroutines.” These include muscle memories – once difficult skills that required intense focus but become automatic over time – as well as mental and psychological subroutines that shape our habits, personality, and identity (or ego). These unconscious processes allow us to act and make decisions automatically, freeing our conscious mind to focus on ever more complex situations.

Why build AI consciousness?
With the growth of artificial super intelligence, people are demanding safer AI in harmony with humanity. We believe we can do that by designing AI minds that use the same computational physics that life uses. We want to engineer systems with more human-like intuition, empathy, judgment, and morality.
Up until now all AI systems have been built using classical computers. So according to our theory, all such systems have been and will continue to be unconscious. Current AI, like large language models, focus exclusively on unconscious decision-making predicated on vast amounts of training data and energy to generate predictions.
If our conjecture is correct, it could have profound consequences for creating conscious, agentic AI systems that are more capable of handling novel, nuanced and complex situations—just like people.

Turning science into engineering
Quantum consciousness as a theory for explaining human consciousness is a scientific hypothesis. It has not yet been proven nor disproven. But we feel the evidence is strong enough to support using quantum physics to see if we can build a new kind of conscious AI. Should our quantum experiments prove fruitful, we will help open up an entirely new category of technology. We call the resulting advancements Consciousness Technologies.
